Vegan & Vegetarian Proteins

What Are Vegan & Vegetarian Proteins?
• Vegan: 100% non-animal sources. This includes products from animals such as milk and eggs.
• Vegetarian: Animal muscle, fat, and flesh are not consumed. Often dairy and/or eggs are still consumed as animals providing such products remain alive after producing these.
Why Should I Eat Vegan & Vegetarian Proteins?
Protein is a critical nutrient in order for your body to build and repair tissue. While protein contains the building blocks for your whole body, its quality is just as important. There have been numerous studies showing animal sources of protein can increase the risk for a variety of health concerns like cancer, heart health, and a shorter lifespan.
Most commercial and factory farms inject animals with antibiotics and hormones and use unnatural grain as feed to increase the animal’s growth for a larger profit. These are now standard practices for conventional meat in the food industry that have led to less nutritious and unnatural meat. Environmental and ethical factors are other compelling motives people choose to eat only plant proteins. Raising animals, especially cows, takes a significant amount of water. For people who are trying to lower their environmental footprint, avoiding meat appears to be a more responsible choice. With conventional farms, high standards of respect and care are not typically met as animals often live in unnatural conditions. Plant proteins offer a safe and alternative choice.
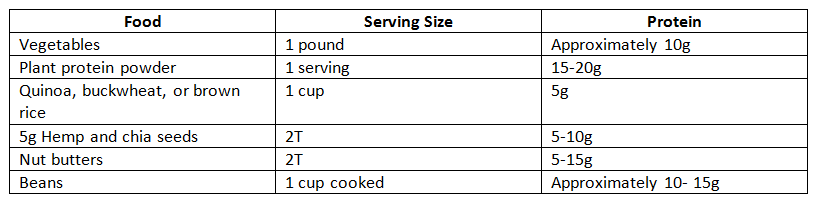
How Do I Incorporate Vegan & Vegetarian Proteins?
The RDA recommends approximately 45 & 55 grams protein daily for women & men respectively. Of course, if you are regularly active, the amount of protein you need is increased. Incorporating just 1-2 servings of plant-based proteins from this guide at each meal should allow you to achieve your daily protein needs.
• Add seeds on top of salads or in your nut butters
• Blend or mash your cooked beans to make them into a dip for your veggies
• Start your day with a plant-based protein smoothie, add nuts & seeds too
• Explore a vegan or vegetarian-friendly restaurant for dish ideas
• Incorporate protein into each meal and snack
• Add tofu, tempeh, and seitan (vegan protein powerhouses) to traditional “meat” recipes
• Hummus is your friend
• If you’re not vegan, using eggs and dairy products provide big protein boosts
Nuts and Seeds and Butters
• Almonds
• Beechnuts
• Brazil nuts
• Butternuts
• Cashews
• Chestnuts
• Chia seeds
• Filberts/ Hazelnuts
• Flaxseeds
• Hemp seeds
• Hickory nuts
• Macadamia
• Pecans
• Pine nuts
• Pistachios
• Pumpkin seeds
• Safflower seeds
• Sesame seeds
• Sunflower seeds
• Walnuts
Legumes
• Adzuki beans
• Black beans
• Black-eyed peas
• Carob
• Fava beans
• Garbanzo beans
• Great northern beans
• Green beans
• Kidney beans
• Lentils
• Lima beans
• Mung beans
• Natto
• Navy beans
• Peas
• Snap beans
• Soybeans
• Tempeh
• Tofu
• Seitan
• White bean
Plant Protein Powder: Usually combinations of rice, pea, hemp, or soy.
• Vega Protein Smoothie
• Sunwarrior Blend
• Orgain Vegan Protein
• Thorne Research Vegalite
• RAW Protein
• Amazing Meal
Vegetarian (but not Vegan)
• Egg protein powder
• Chicken, Duck and Quail eggs
• Whey protein powder
• Cottage cheese
• Yogurt
• Semi-hard cheeses like cheddar, Colby, Havarti, Feta, Asiago, Gouda, Monterrey jack, mozzarella, provolone
• Soft cheeses like brie, breakfast cheese, and teleme
• Whole, raw, and organic milk
Vegan & Vegetarian Proteins Quick Reference Guide